Documentation
Welcome to the AI Linux Agent documentation. This guide will help you set up, configure, and maximize the value of your AI-powered infrastructure management platform.
Our platform combines traditional monitoring with generative AI to provide:
- Real-time telemetry and log analysis
- Natural language command execution
- Automated security compliance (OpenSCAP)
- Generative Ansible playbooks
Getting Started
1. Registration
First, create an account on our cloud platform. You will be assigned a unique Organization ID.
During login, you can optionally enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA) for enhanced account security. We also offer granular Role-Based Access Control (RBAC), allowing you to define precise permissions for every system function and user.
2. Installing the Agent
Once registered, you can install the agent on any Linux server (Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, RHEL). The installation script handles dependencies automatically.
curl -sSL https://app.unixai.org/download/agent.sh | sudo bash -s -- --organization-id YOUR_ORG_IDReplace YOUR_ORG_ID with the ID found in your dashboard settings.
Dashboard Overview
The main dashboard provides a birds-eye view of your infrastructure. You can see real-time metrics for CPU, Memory, Disk I/O, and network activity.
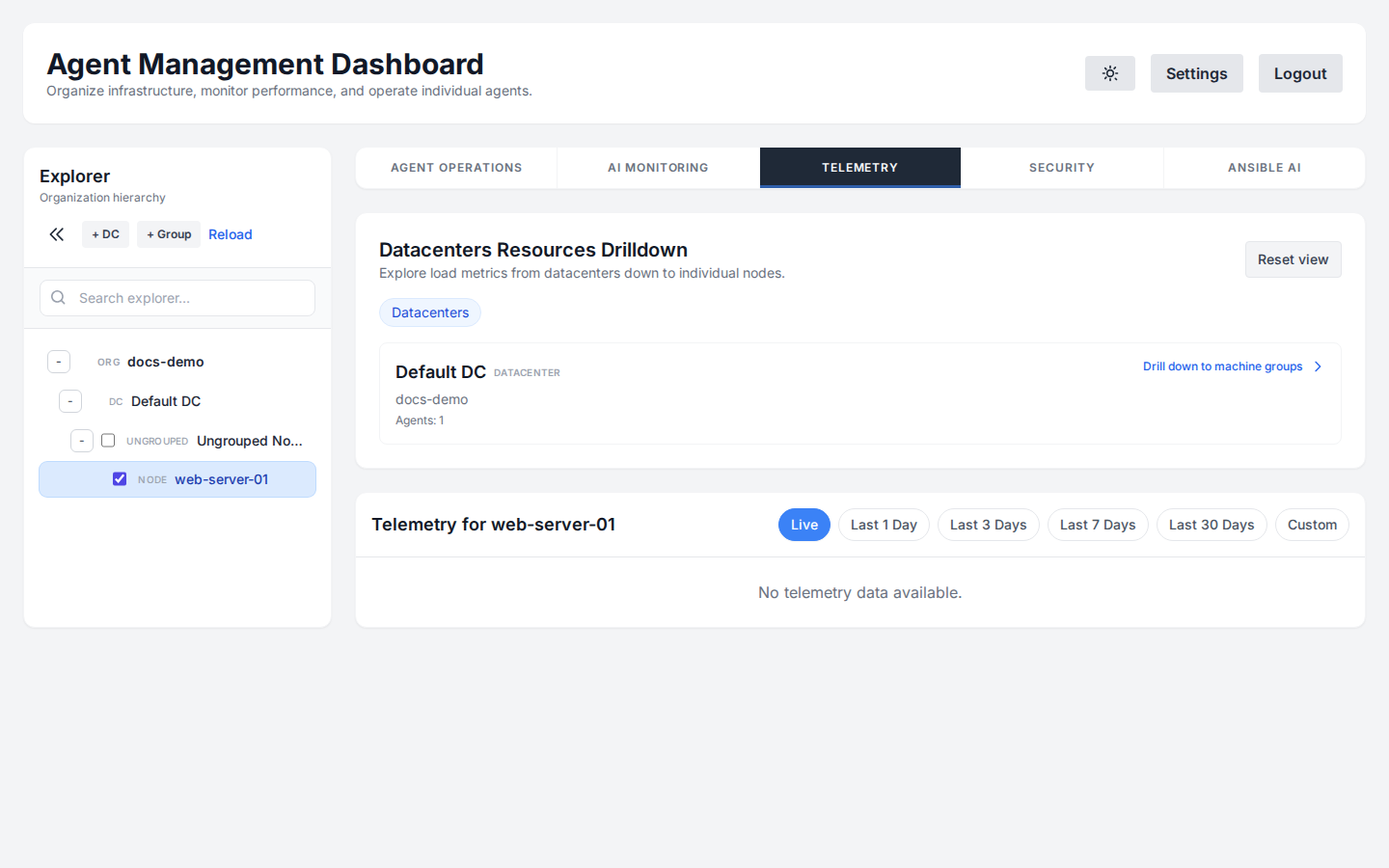
The Explorer panel on the left allows you to organize your fleet. You can create Datacenters and Machine Groups to structure your servers logically. To interact with or view details for any specific server or group, simply click on it in the Explorer tree.
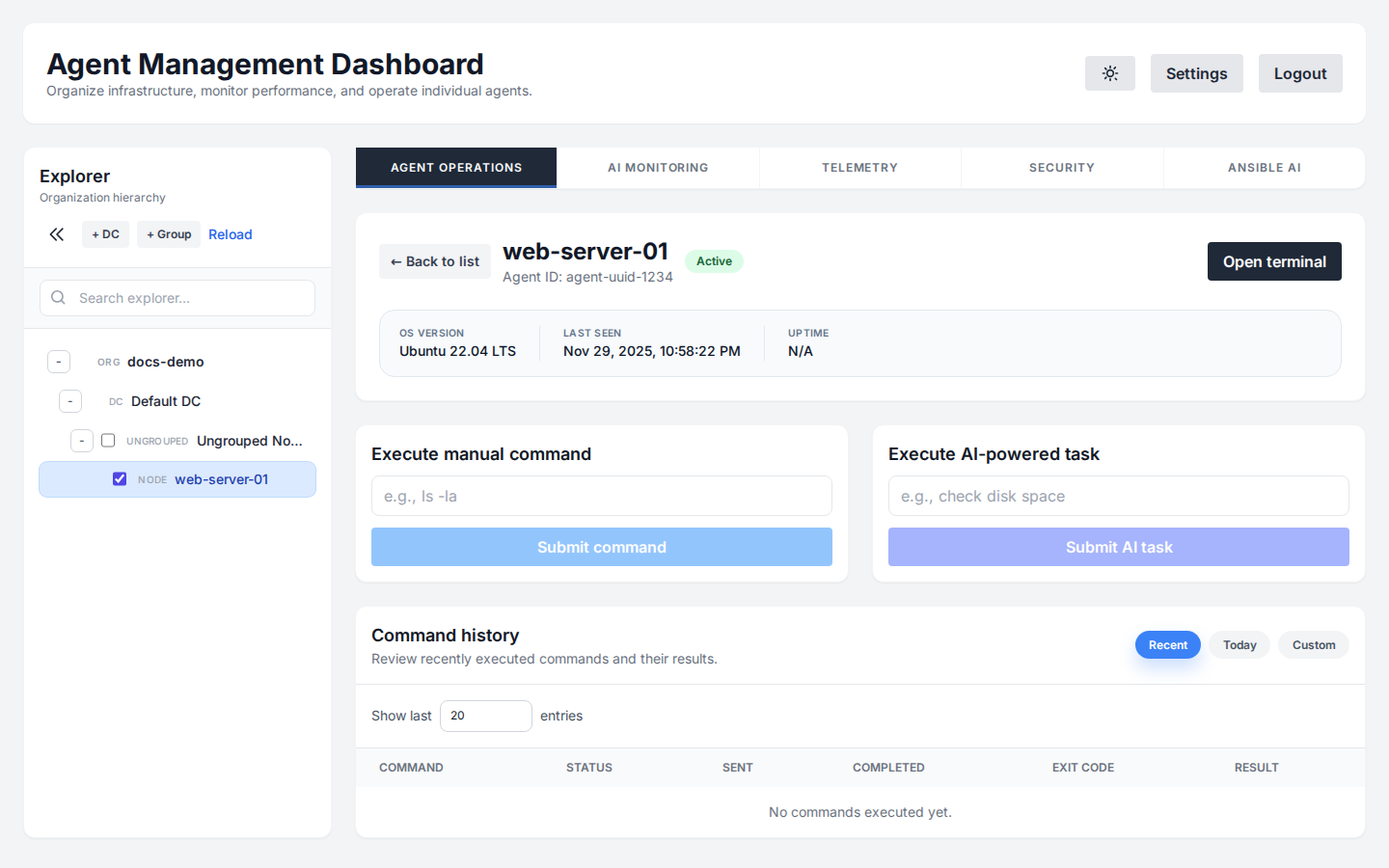
AI Command Execution
Interact with your servers using natural language. The "Execute" tab provides a chat interface where you can ask the agent to perform tasks.
Example prompts:
- "Find the process consuming the most memory and kill it."
- "Check if the Nginx service is running and restart it if not."
- "List all large files in /var/log."
Open Terminal
For direct, low-level access, use the Open Terminal feature. This opens a fully interactive session to your server directly in the browser, functioning equivalently to a standard SSH connection.
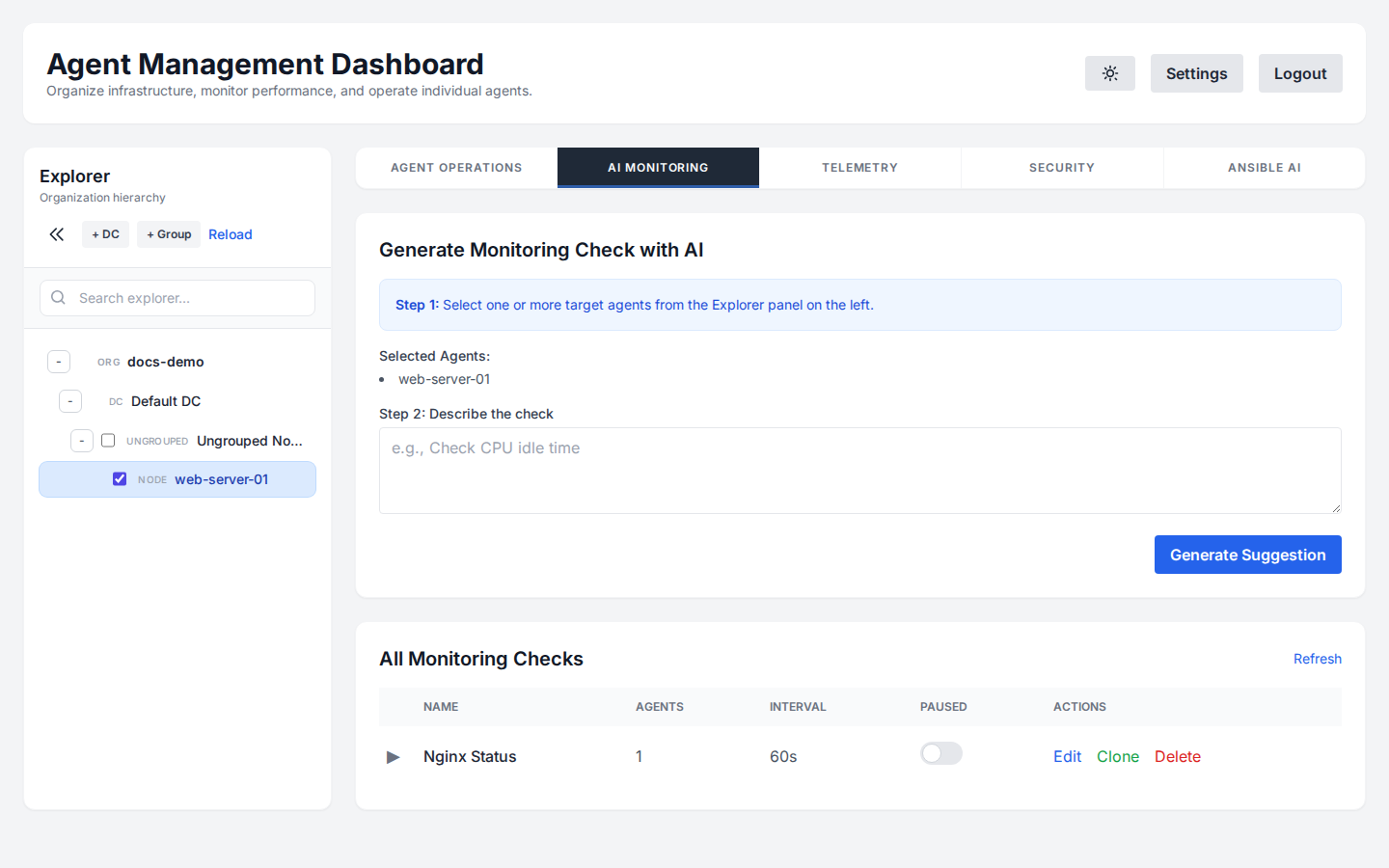
Monitoring Checks
Create custom monitoring scripts without writing code. Describe what you want to check, and the AI will generate the Bash or Python script for you.
AI Analyze for Alarms
When a monitoring check triggers an alarm (Warning or Critical), you can use the AI Analyze feature. The AI will examine the check's output and system context to diagnose the root cause and suggest immediate remediation steps.
Predictive Monitoring
The system includes built-in Predictive Monitoring capabilities enabled by default. Using advanced algorithms like Linear Regression (for disk usage) and Holt's Linear Trend (for CPU/Memory), the agent analyzes historical telemetry data to forecast future resource usage.
It can alert you if a disk is expected to fill up in the next 7-14 days or if CPU/Memory saturation is trending towards 100%, allowing you to take action before an outage occurs. No additional configuration is required.
AI Documentation
Keep your infrastructure documentation in sync with reality. The AI Documentation feature automatically discovers installed packages, network configurations, running services, and more.
It then synthesizes this raw data into a structured, easy-to-read Markdown document, covering everything from OS details to Nginx vhost configurations. You can view, export, or regenerate this documentation directly from the dashboard to ensure you always have an up-to-date reference.
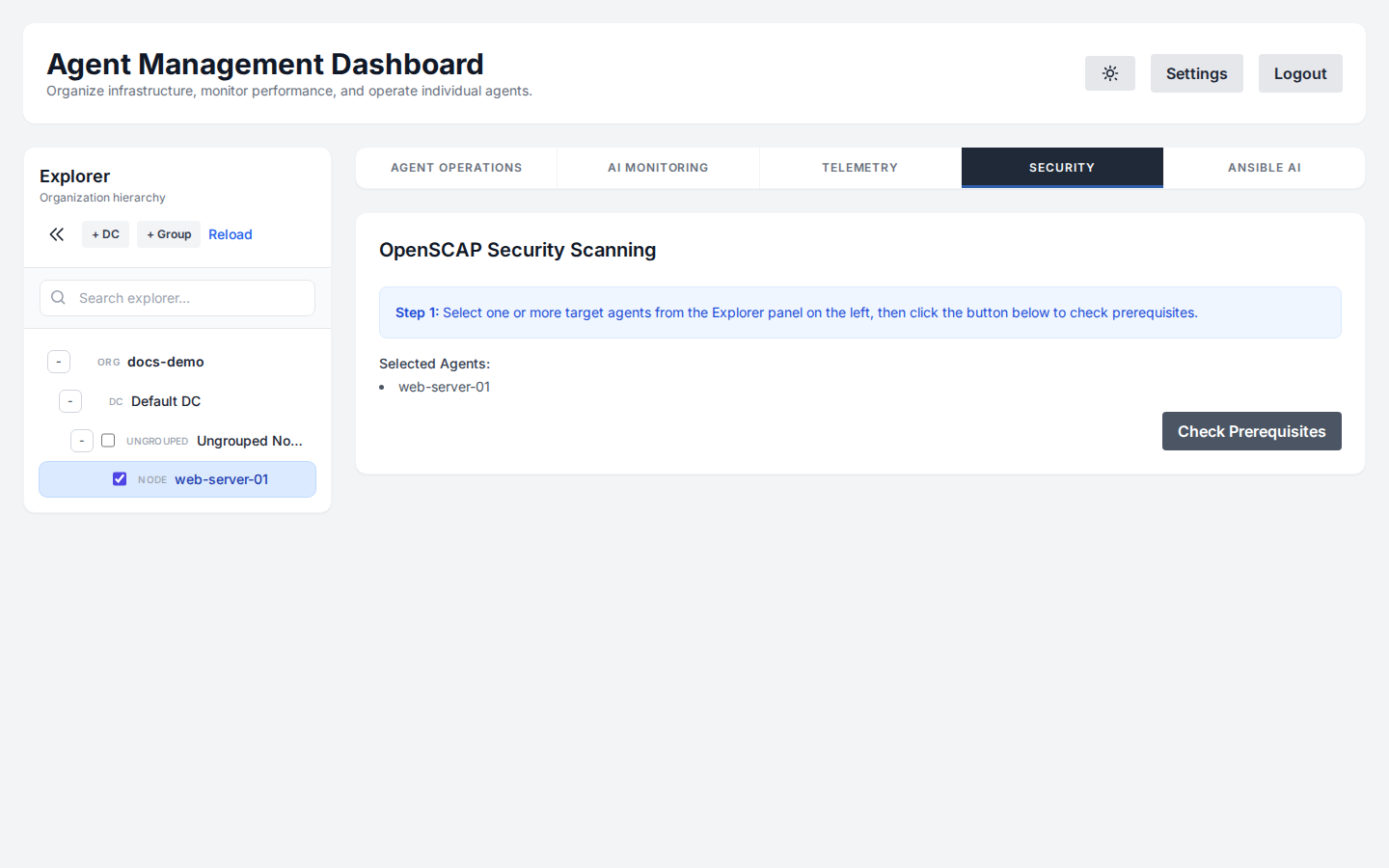
Security Scanning
Ensure compliance with OpenSCAP. The agent can run scans against profiles like PCI-DSS or HIPAA and report vulnerabilities.
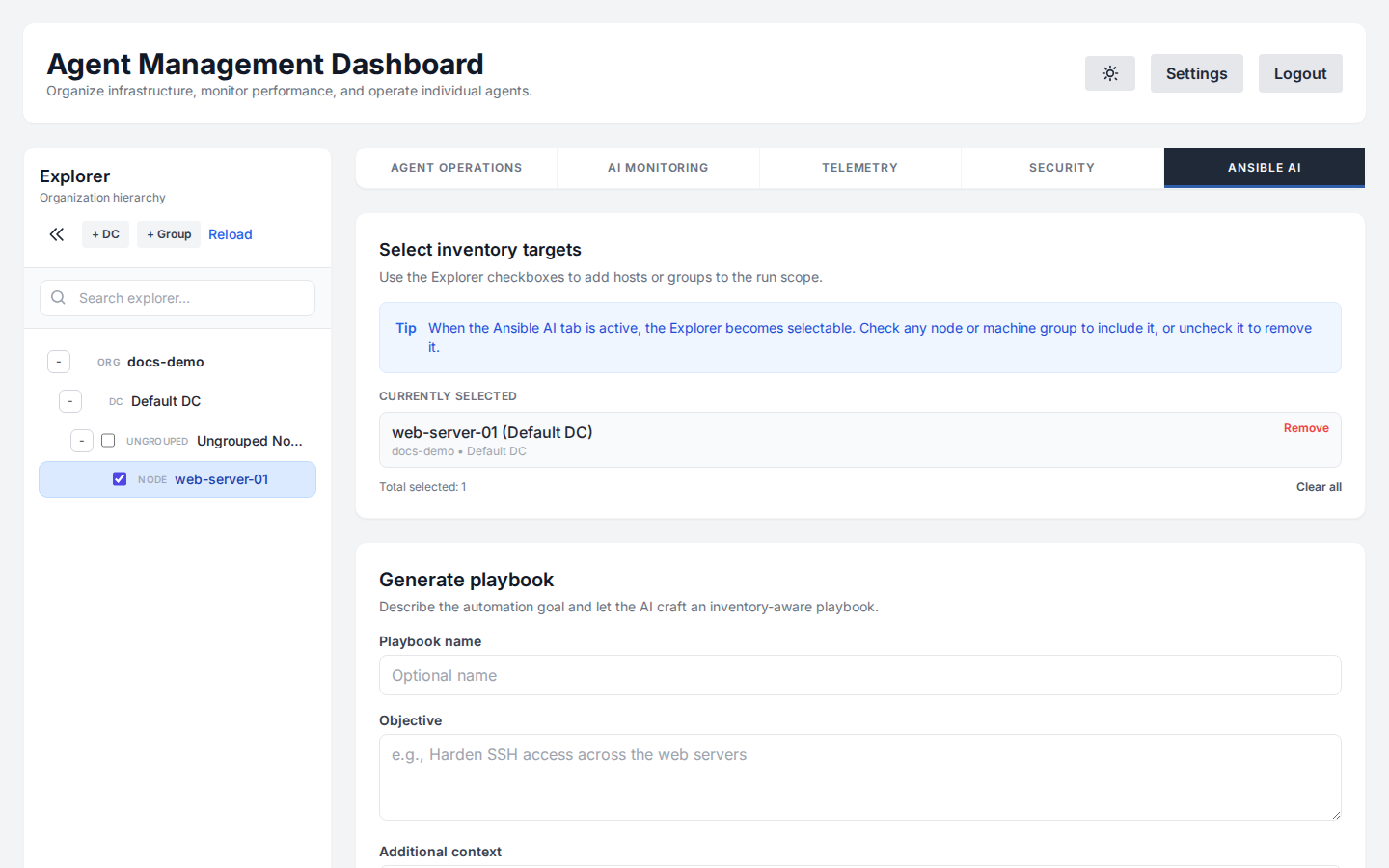
Ansible Automation
Generate Ansible playbooks for complex deployments. The AI ensures idempotency and follows best practices.
Troubleshooting
Agent not connecting?
- Check if the service is running:
systemctl status ai-linux-agent - View logs:
journalctl -u ai-linux-agent -f - Ensure outbound traffic to port 443 is allowed.